
- #HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 HOW TO#
- #HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 FULL#
- #HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 CODE#
Step 1: Find the store where ad-ins are available.
#HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 HOW TO#
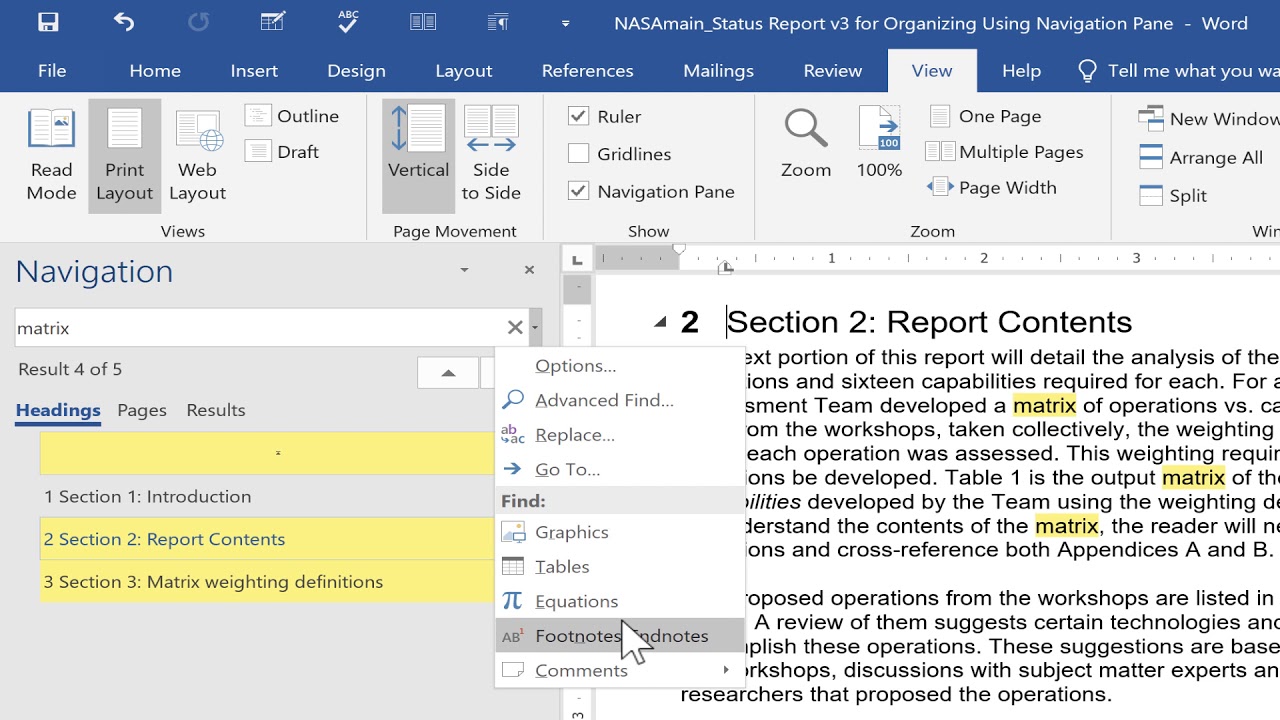
How to Find and Install Plugins for Wordīefore introducing the most recommended add-ins that you should have, let us first discuss how to find and install a plug-in. Now, let’s scroll down the page and check out what you need for your Microsoft Word. You’ll soon be on track for increased efficiency. That way, the easy can become easier and the convenient can become more convenient. As such, we highly that you should install add-ins for Microsoft Word. No matter how advantageous this is, it still lacks some features. In order to help us easily compose documents. It helps people create documents and it possesses functions that an old-school type writer machine could never dream of. The tabs array defines one or more contextual tabs, up to a maximum of 20.Whether it is for a business, profession or school, Microsoft Word is widely used. The actions array is a specification of all the functions that can be executed by controls on the contextual tab.

#HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 CODE#
For more information, see Editing JSON with Visual Studio Code - JSON schemas and settings.īegin by creating a JSON string with two array properties named actions and tabs. If you are working in Visual Studio Code, you can use this file to get IntelliSense and to validate your JSON.
#HOW TO CREATE NAVIGATION TABS IN WORD 2013 FULL#
The full schema for the contextual tab JSON is at. We'll construct an example of a contextual tabs JSON blob step-by-step. The structure of the JSON blob's properties and subproperties (and the key names) is roughly parallel to the structure of the CustomTab element and its descendant elements in the manifest XML. If it is called again, an error is thrown. Also, the requestCreateControls method may be run only once in a session of your add-in. This is different from custom core tabs which are added to the Office application ribbon when the add-in is installed and remain present when another document is opened. Custom contextual tabs are only present in documents on which your add-in is currently running. Your code parses the blob into a JavaScript object, and then passes the object to the method. Unlike custom core tabs, which are defined with XML in the manifest, custom contextual tabs are defined at runtime with a JSON blob. Define the groups and controls that appear on the tab For more information, see Configure an add-in to use a shared runtime. Specify the circumstances when the tab will be visible.Ĭonfigure the add-in to use a shared runtimeĪdding custom contextual tabs requires your add-in to use the shared runtime.

The user experience for custom contextual tabs follows the pattern of built-in Office contextual tabs. (The technique of specifying the requirement sets in the manifest, which is also described in that article, does not currently work for RibbonApi 1.2.) Alternatively, you can implement an alternate UI experience when custom contextual tabs are not supported. You can use the runtime checks in your code to test whether the user's host and platform combination supports these requirement sets as described in Runtime checks for method and requirement set support. For more about requirement sets and how to work with them, see Specify Office applications and API requirements. Custom contextual tabs work only on platforms that support the following requirement sets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
